CO2 Lasers Explained: What They Are, How They Work, and Why You Need One
Have you ever wondered how intricate designs are cut into wood, metal, or even skin during medical procedures? The answer often lies in the power of CO2 lasers. If you’re considering using laser technology, you’re likely feeling a mix of curiosity and confusion. With so many types of lasers out there, understanding what a CO2 laser is and how it works can be overwhelming.
That’s where I come in. With years of experience in laser technology, I’m here to break down the complexities and give you a clear, concise understanding of CO2 lasers. In this article, you’ll learn exactly what a CO2 laser is, how it operates, and what it’s best suited for. Whether you’re a manufacturer, a medical professional, or a DIY enthusiast, this guide will help you determine if a CO2 laser is the right tool for your needs.
What is a CO2 Laser?
A CO2 laser is a type of gas laser that uses carbon dioxide (CO2) as its lasing medium. It’s one of the oldest and most common types of lasers, renowned for its efficiency and power. In simple terms, a CO2 laser generates a concentrated beam of infrared light, typically at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometres. This wavelength is particularly effective for cutting, engraving, and marking a wide range of materials, from wood and acrylic to metals and even human tissue.
Key Characteristics:
- High Power Output: CO2 lasers can produce a significant amount of power, making them ideal for industrial applications where strong and precise cutting is required.
- Versatile Application: They are highly versatile and can be used for everything from precision surgery to large-scale metal fabrication.
- Infrared Light: The light emitted by a CO2 laser is in the infrared spectrum, which is invisible to the human eye but highly effective in interacting with materials.
Compared to other types of lasers, such as fibre lasers or Nd lasers, CO2 lasers stand out due to their ability to cut and engrave non-metallic materials with great precision. This makes them particularly popular in industries like manufacturing, medical aesthetics, and even arts and crafts.
Here’s a simple comparison:
| Type of Laser | Wavelength | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser | 10.6 µm | Cutting/engraving non-metals |
| Fibre Laser | 1.06 µm | Metal cutting/marking |
Nd Laser | 1.06 µm | Welding/metal processing |
This versatility and power have made CO2 lasers a go-to choice for many applications, as we’ll explore further.
How Does a CO2 Laser Work?
At the core of every CO2 laser lies a fascinating process of light amplification that transforms invisible gas into a powerful cutting beam. Let’s break it down into simple steps:
1. Lasing Medium
The heart of the CO2 laser is the lasing medium—a mixture of gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and helium (He). When the laser is activated, electrical energy excites these gases, causing the CO2 molecules to reach a higher energy state.
2. Excitation Process
When the CO2 molecules are excited, they emit photons, which are particles of light. These photons are then reflected back and forth between two mirrors positioned at either end of the laser tube, causing them to interact with other excited CO2 molecules. This interaction amplifies the light, creating a strong, coherent beam of infrared radiation.
3. Beam Emission
One of the mirrors in the laser tube is partially transparent, allowing some of the amplified light to escape. This emitted light is the laser beam, which is then directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus it onto the material you want to cut or engrave.
4. Focusing and Cutting
The focused laser beam is incredibly powerful, concentrating all its energy into a small, precise point. When this beam makes contact with a material, it heats it to the point of vaporization, effectively cutting or engraving the material with extreme precision.
Here’s a visual representation of how a CO2 laser works:
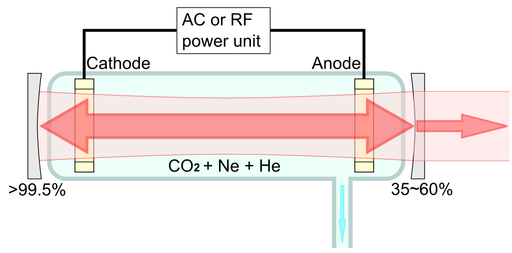
Figure 1: Simplified Diagram of CO2 Laser Operation.
5. Cooling System
CO2 lasers generate a lot of heat, so they are typically equipped with a cooling system—often using water or air—to prevent the laser from overheating and to maintain stable operation.
The science behind CO2 lasers might sound complex, but in practice, it’s this precise control over light and energy that makes them such a powerful tool for a wide variety of applications.
What are CO2 Lasers Good For?
CO2 lasers are incredibly versatile tools, used across a wide range of industries for various applications. Their ability to cut, engrave, and mark different materials with high precision makes them particularly valuable in manufacturing, medical fields, and even in creative arts. Here’s a closer look at where CO2 lasers excel:
1. Material Cutting
CO2 lasers are widely used for cutting non-metallic materials, thanks to their high power and precision. Some of the materials that CO2 lasers can cut include:
- Wood: Ideal for cutting intricate designs in wood, from furniture making to custom signage.
- Acrylic and Plastics: Perfect for creating clear, smooth edges in acrylic sheets, used in everything from signage to display cases.
- Leather and Fabric: Used in fashion and upholstery industries for precision cutting without fraying the edges.
- Paper and Cardboard: Commonly used for creating detailed patterns in paper products and packaging materials.
2. Engraving and Marking
Beyond cutting, CO2 lasers are excellent for engraving and marking materials. This process involves removing a small amount of material from the surface to create a design or text.
- Glass and Ceramics: CO2 lasers can engrave detailed patterns or text on glassware and ceramic tiles without cracking or damaging the material.
- Rubber and Stamps: Perfect for creating custom rubber stamps with intricate details.
- Stone and Marble: Often used in the creation of commemorative plaques or personalised gifts with detailed engravings.
3. Medical Applications
In the medical field, CO2 lasers are highly valued for their precision and ability to minimise damage to surrounding tissues.
- Laser Surgery: CO2 lasers are used in procedures such as skin resurfacing, where they precisely remove layers of skin to treat scars, wrinkles, and other skin conditions.
- Otolaryngology (ENT): These lasers are also used in surgeries involving the ear, nose, and throat, where precision and minimal invasiveness are critical.
4. Creative Arts and Crafts
Artists and hobbyists use CO2 lasers to bring their creative visions to life with unmatched precision.
- Custom Engravings: Personalising items like jewellery, gifts, or home decor with detailed engravings.
- Model Making: Cutting and assembling miniature models from wood, acrylic, or other materials.
5. Industrial and Manufacturing Uses
In industrial settings, CO2 lasers are employed for large-scale production and fabrication.
- Automotive Industry: Used for cutting and engraving various components, including dashboards and interior elements.
- Electronics: CO2 lasers can mark electronic components without damaging the sensitive materials inside.
Example Projects Using CO2 Lasers:
- Custom wooden coasters with engraved designs.
- Acrylic signage with smooth, polished edges.
- Engraved glass awards or trophies.
Image Gallery: Here are some examples of what CO2 lasers can achieve:

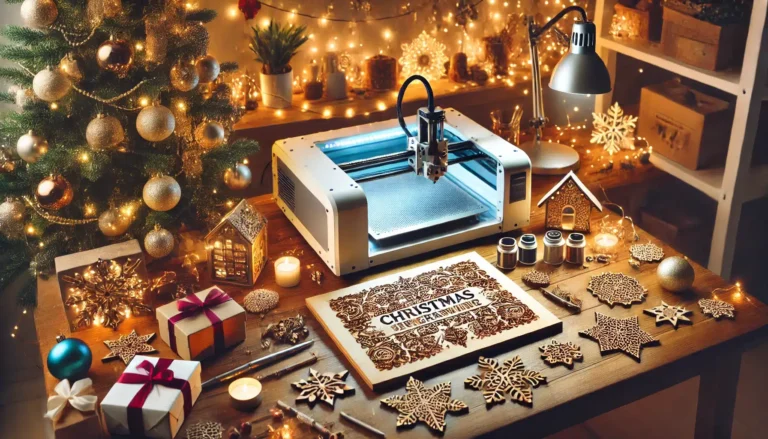
Figure 2: Precision wood cutting with a CO2 laser.

Figure 3: Detailed glass engraving using a CO2 laser.
CO2 lasers truly shine in applications where precision and versatility are required. Whether you’re crafting a custom gift or performing a delicate medical procedure, a CO2 laser can provide the exact results you need.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers are powerful and versatile, but like any technology, they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you determine whether a CO2 laser is the right tool for your needs.
Advantages of CO2 Lasers
High Precision
- CO2 lasers offer incredibly high precision, making them ideal for intricate cutting and engraving tasks. This precision is essential for applications in industries like medical surgery, where exactness is critical.
Versatility
- CO2 lasers can cut and engrave a wide range of non-metallic materials, including wood, glass, acrylic, fabric, and even human tissue. This makes them a versatile tool in both industrial and creative fields.
Smooth Edges
- One of the standout features of CO2 lasers is their ability to create smooth, clean edges on cut materials. This is particularly beneficial when working with acrylics or fabrics where fraying or rough edges can be problematic.
Minimal Material Waste
- The precision of CO2 lasers allows for minimal material waste, which is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly. This is especially important in industries where material costs are high.
Non-Contact Process
- CO2 lasers operate as a non-contact cutting method, meaning the laser beam does not physically touch the material. This reduces the risk of contamination and damage to delicate materials.
Disadvantages of CO2 Lasers
Limited to Non-Metals
- While CO2 lasers excel at cutting and engraving non-metallic materials, they are not as effective on metals, especially thicker or more reflective metals like aluminium. For metal cutting, fibre or Nd lasers are typically better options.
High Initial Cost
- The upfront cost of purchasing a CO2 laser system can be high, particularly for industrial-grade machines. However, this cost is often justified by the precision and versatility the laser provides.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
- CO2 lasers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, including the replacement of parts like mirrors and the lasing medium. Additionally, they consume a significant amount of power, which can lead to higher operating costs.
Safety Considerations
- Operating a CO2 laser requires strict adherence to safety protocols to prevent accidents, such as burns or eye damage. The infrared light emitted by CO2 lasers is invisible to the naked eye, making it especially important to use protective eyewear and other safety equipment.
Cooling Requirements
- Due to the heat generated during operation, CO2 lasers often require a robust cooling system, typically using water or air. This adds complexity to the setup and can increase the overall cost of operation.
Summary: While CO2 lasers offer unmatched precision and versatility, particularly for non-metallic materials, they also come with some limitations, especially regarding their cost and the materials they can effectively process. By weighing these advantages and disadvantages, you can better determine if a CO2 laser is the right tool for your specific needs.
Safety Considerations
While CO2 lasers are powerful tools with numerous applications, it’s crucial to operate them with care to avoid accidents or injuries. Here are some essential safety considerations to keep in mind when using a CO2 laser.
1. Eye Protection
- The Invisible Danger: CO2 lasers emit infrared light, which is invisible to the naked eye. Despite being invisible, this light can cause severe damage to your eyes, potentially leading to permanent blindness if proper precautions aren’t taken.
- Protective Eyewear: Always wear appropriate laser safety glasses designed for the specific wavelength of CO2 lasers (10.6 µm). These glasses will block or absorb the harmful infrared light, protecting your eyes.
2. Skin Protection
- Laser Burns: The intense heat generated by a CO2 laser can cause serious burns if the laser beam comes into contact with your skin. This can happen in an instant, so it’s important to always be aware of where the beam is directed.
- Proper Clothing: Wear protective clothing that covers exposed skin when operating the laser. It’s also wise to avoid wearing reflective jewellery, which could inadvertently redirect the laser beam.
3. Ventilation
- Fume Extraction: When a CO2 laser cuts or engraves materials, it can produce fumes, smoke, and particulate matter that may be harmful if inhaled. This is particularly true when working with plastics or other synthetic materials.
- Ventilation Systems: Ensure your workspace is equipped with a proper ventilation system or fume extractor to remove hazardous fumes from the air. This is critical not only for your health but also for maintaining a clear working environment.
4. Fire Safety
- Risk of Ignition: The intense heat from the laser beam can ignite flammable materials, leading to a fire hazard. Always keep a fire extinguisher nearby when operating a CO2 laser.
- Material Selection: Avoid using highly flammable materials in the laser cutter, and ensure the area around the laser is free of combustible materials like paper, cloth, or sawdust.
5. Electrical Safety
- High Voltage: CO2 lasers operate at high voltages, and improper handling of the electrical components can lead to electric shock or equipment damage.
- Regular Inspections: Perform regular inspections of the laser’s electrical components, including wiring and connections, to ensure they are in good condition. Never attempt to repair or modify electrical parts without proper training.
6. Laser Operation and Maintenance
- Training: Proper training is essential before operating a CO2 laser. Make sure you understand how to safely start, operate, and shut down the laser, as well as how to handle emergencies.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the laser operates safely and efficiently. This includes checking the alignment of mirrors, cleaning the lenses, and replacing parts as needed.
7. Emergency Protocols
- Emergency Shut-Off: Familiarise yourself with the laser’s emergency shut-off procedure. In case of an accident or malfunction, you need to be able to quickly disable the laser to prevent injury or damage.
- First Aid Kit: Keep a first aid kit in the workspace, stocked with supplies for treating burns and other minor injuries. It’s also wise to know the location of the nearest emergency medical services.
While CO2 lasers are invaluable tools, they must be treated with respect and caution. By following these safety guidelines, you can minimise the risk of injury and ensure a safe working environment.
CO2 lasers are a remarkable blend of precision, power, and versatility, making them indispensable tools in various industries—from manufacturing and medical fields to creative arts and beyond. Whether you’re looking to cut intricate designs into wood, engrave glassware with detailed patterns, or perform delicate surgical procedures, CO2 lasers offer a reliable and efficient solution.
Understanding how a CO2 laser works, its benefits, and its limitations is crucial to making the most out of this technology. While they excel in cutting and engraving non-metallic materials, it’s important to weigh their advantages against factors like cost, maintenance, and safety requirements. By following proper safety protocols, you can harness the full potential of CO2 lasers while ensuring a safe and productive work environment.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious beginner, CO2 lasers can open up a world of possibilities. With the right knowledge and precautions, you can confidently take on new projects and achieve stunning results with this powerful technology.